How Many Bones Are in a Dog: Exploring Canine Skeletal Structure
Discover the fascinating world of canine anatomy and learn how many bones are in a dog. Explore the skeletal structure of man’s best friend in this informative guide.
Did you know a dog’s skeleton is as complex as ours? It shows how agile, strong, and adapted they are. The study of a dog’s skeleton tells us a lot about their abilities.
A typical dog has around 319 bones. This count can change with breed and size. The skeletal system is key for their movement and safety.
The number of bones in a dog can change for many reasons. Bigger dogs have more bones for support. Smaller dogs have fewer. The tail’s length also affects the count, with some having up to 23 tail vertebrae.
Learning about dog bones and their skeleton helps us care for them better. Every bone, from the skull to the tail, is important for their health.
Understanding the Canine Skeletal System
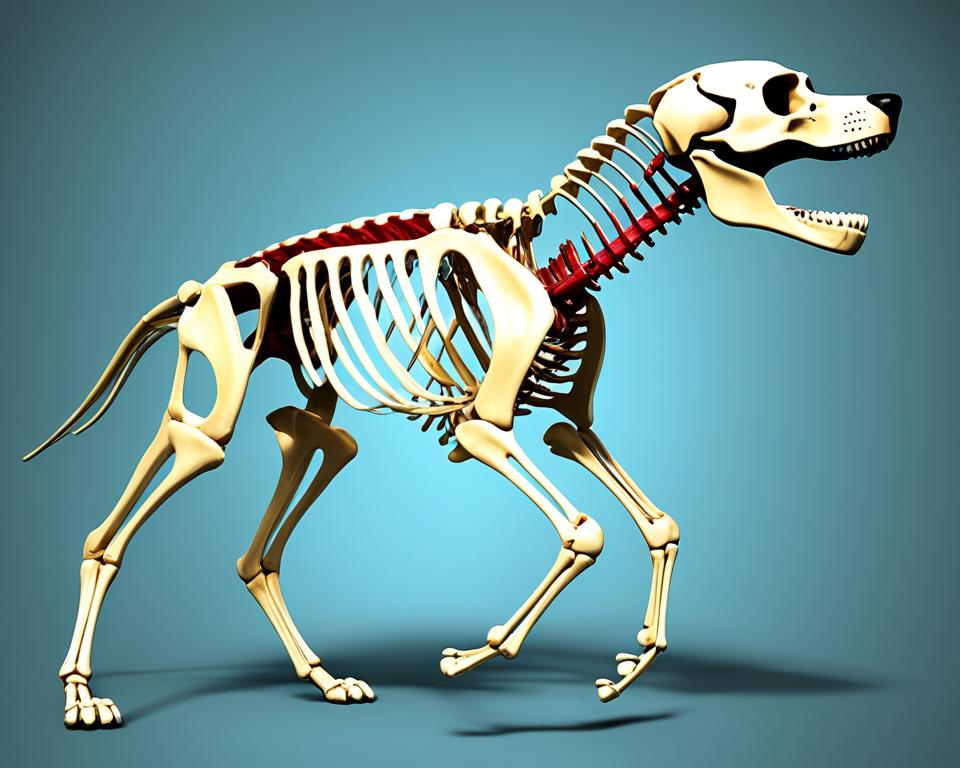

The canine skeletal system is key to a dog’s body, giving it structure and support. Dogs have about 319 bones, which can vary by breed. This network of bones is crucial for their health and how they move.
The Composition of Dog Bones
Dog bones are made of two main types: cortical and cancellous. Cortical bone is 80% of the bone’s mass, making it strong and stiff. The other 20% is cancellous bone, which is flexible and helps make blood cells.
Functions of the Skeletal System in Dogs
The skeletal system in dogs has many roles. It protects important organs, supports the body, and helps with movement. The rib cage, with 13 pairs of ribs, keeps the heart and lungs safe. The femur, the biggest bone, is key for walking.
Comparison to Human Bone Structure
Dogs and humans have similar bones but also some big differences. Dogs don’t have collarbones, which lets them take longer strides. They have 18 toes, five on each front paw and four on each back paw. Dogs also have dewclaws, which are extra bones for stability during certain activities.
How Many Bones Are in a Dog
Dogs have a unique skeletal system. On average, adult dogs have 321 bones. This is more than humans, who have 206 bones. This difference shows how dogs are adapted for moving and being agile.
Dogs have bones all over their body. The axial skeleton, which includes the spine, skull, and ribs, has 134 bones. The limbs add another 186 bones. Male dogs even have an extra bone called the os penis.
Different dog breeds have different skeletons. The smallest dog ever recorded was a Yorkshire Terrier, only 6.3 cm tall. On the other end, a Great Dane was the tallest at 106.7 cm. These size differences affect how many bones they have.
Knowing how many bones dogs have is important for vets and dog owners. It helps them understand how dogs move, grow, and can affect their health. This knowledge is key to keeping our dogs healthy and happy.
The Role of Bones in Canine Anatomy
The dog skeletal system is crucial for canine anatomy. It gives structure, protection, and support to our furry friends. Learning about canine bone function shows us how complex a dog’s body is.
Protection of Vital Organs
Bones protect vital organs. The skull, made of fused bones, keeps the brain safe. The rib cage covers the heart and lungs. This protection lets dogs play and explore safely.
Support and Locomotion
Bones make up a dog’s body framework. The spine supports the body with 7 cervical, 13 thoracic, and 7 lumbar vertebrae. Limb bones like the femur and humerus help with movement.
The shoulder blades let dogs move forward and backward. The rear bones affect how they walk. This setup is key for a dog’s mobility.
Blood Cell Production
Bone marrow in dogs makes blood cells. It’s a spongy tissue inside bones that creates red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. These cells are vital for a dog’s immune system and health.
The canine skeletal system is similar across all breeds. From tiny Chihuahuas to big Great Danes, the basic bone structure is the same. This consistency lets breeds have their unique traits while keeping the core anatomy the same.
Unique Skeletal Features in Different Dog Breeds
Dog breed skeletal differences are fascinating and diverse. The most noticeable variations occur in skull shapes. Breeds fall into three main categories: dolichocephalic (long-headed), mesocephalic (medium-skulled), and brachycephalic (broad-skulled) dogs. These skull types influence not only appearance but behavior too.
Dolichocephalic dogs, like Afghan Hounds, have elongated snouts and heads. They’re often less playful but more focused on tasks. Brachycephalic dogs, such as Pugs, have short, wide skulls. These breeds tend to be more human-oriented and protective. Mesocephalic dogs, including Golden Retrievers, have balanced skull proportions.
Beyond skull shape, other unique features exist. Some breeds, like the Great Pyrenees, have double dewclaws on their hind legs. This extra ‘thumb’ helped them navigate snowy terrain. Dachshunds have long, low bodies perfect for burrowing. These skeletal adaptations showcase how breeding has shaped dogs for specific tasks and environments.
FAQs
What is the average number of bones in a dog’s body?
Dogs usually have about 320 bones. This number can change a bit because of things like tail length and breed.
How does the canine skeletal system differ from humans?
Dogs don’t have a collarbone like humans do. This lets them take bigger strides when they run. Dogs also have different skull shapes based on their breed.
What are the main functions of the skeletal system in dogs?
The skeletal system in dogs is very important. It protects the brain, supports the body, helps with movement, keeps balance with the tail, and makes blood cells in the bone marrow.
How do dog breeds differ in their skeletal features?
Different dog breeds have unique skeletal features. For example, their skulls can be long, medium, or broad. These differences affect their behavior and traits.
How does the skeletal system affect a dog’s movement and gait?
The skeleton is key to how a dog moves and walks. Problems like elbow and hip dysplasia can make it hard for a dog to move and can affect its health.





