How Long Do Guinea Pigs Live? Average Lifespan Revealed
Discover the average lifespan of guinea pigs as pets, factors influencing their longevity, and how to ensure a long and healthy life for your beloved cavies.
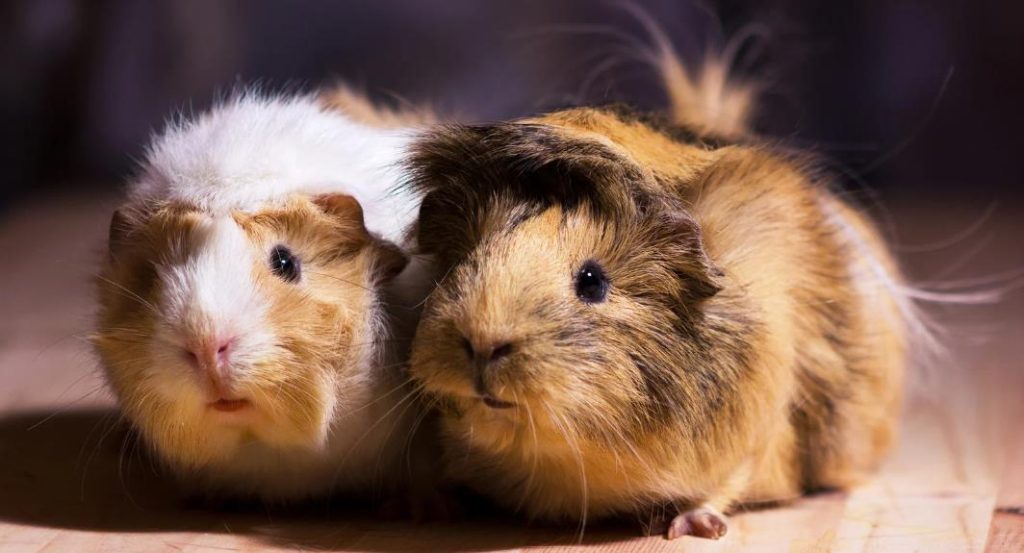

Did you know that some guinea pigs can live up to 10 years or even longer? Contrary to the common misconception that these furry companions have a lifespan of just a few years, guinea pigs can actually thrive for a surprisingly long time when provided with proper care. Understanding the different stages of a guinea pig’s life is crucial in ensuring their well-being and longevity.
Discover how long do guinea pigs live in this blog. During the infancy stage, from birth to 6 months, guinea pigs are highly dependent on their mother for nourishment and protection. As they enter adolescence, from 6 months to 1 year, they become more independent and start to establish their hierarchy within a group. The adult stage, from 1 to 4 years, is when guinea pigs reach their peak physical condition, and it’s important to maintain a healthy diet and provide them with a spacious and stimulating living environment. Finally, as they enter their senior years, 4 years and older, guinea pigs may start to show signs of aging, such as reduced activity levels and dental problems.
Genetics, diet, exercise, and the living environment can influence a guinea pig’s lifespan. By understanding these key elements, guinea pig owners can ensure their furry friends live long and fulfilling lives.
Understanding Guinea Pig Lifespan
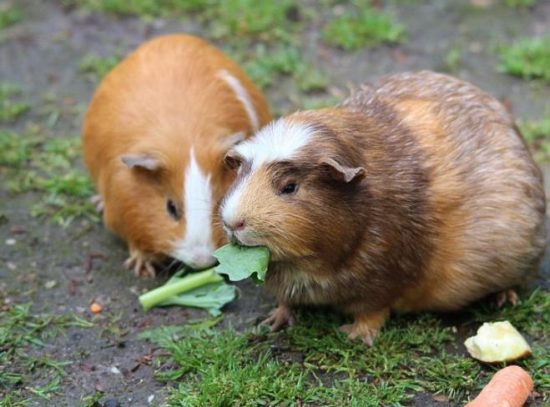

The average lifespan of domesticated guinea pigs is typically 5 to 7 years, with some reaching up to 10 years or even longer. Several factors can influence a guinea pig’s lifespan, including genetics and breeding, diet and nutrition, exercise and enrichment, and living environment.
Genetics play a significant role in a guinea pig’s lifespan, as certain breeds may be more prone to specific health issues or have longer lifespans compared to others. While the average lifespan range is 5 to 7 years, some guinea pigs can live up to 10 years or more with proper care and attention.
In addition to genetics, a guinea pig’s diet and nutrition, exercise and enrichment, and living environment can all impact their longevity. A balanced diet consisting primarily of hay, fresh vegetables, and high-quality pellets is crucial for the overall health and well-being of these furry companions. Regular exercise and a stimulating living environment are also important to maintain their physical and mental well-being. Providing a clean and stress-free living space can help prevent respiratory and skin problems, further contributing to a longer lifespan.
Stages of a Guinea Pig’s Life
Understanding the different stages of a guinea pig’s life is crucial in ensuring their well-being and longevity. From the delicate infancy stage to the golden years, each phase presents unique considerations for their care and nurturing.
Infancy (Birth to 6 months)
Infancy in guinea pigs spans from birth to six months of age, a critical period of rapid growth and development. Newborn guinea pigs, called pups, are precocial, meaning they are born fully furred, with their eyes open, and able to walk within hours of birth. During this stage, they transition from nursing to eating solid foods, requiring a diet rich in vitamin C and other nutrients to support their growth. Socialization is crucial during infancy, as guinea pigs learn to interact with their littermates and humans, shaping their future behavior and temperament.
Adolescence (6 months to 1 year)
Adolescence in guinea pigs occurs from six months to one year, marking a period of continued physical growth and increasing maturity. Adolescent guinea pigs become more active and curious, exploring their environment and solidifying social hierarchies within their groups. This stage involves significant hormonal changes, and it’s essential to monitor their diet and health closely to ensure proper development. Regular handling and interaction during adolescence help reinforce trust and bond with their human caregivers, setting the foundation for a well-adjusted adult guinea pig.
Adulthood (1 to 4 years)
Adulthood in guinea pigs spans from one to four years of age, during which they are at their peak in terms of health and activity levels. Adult guinea pigs are fully mature, with established personalities and social behaviors. This stage requires consistent care, including a balanced diet, regular veterinary check-ups, and ample opportunities for exercise and mental stimulation. Adult guinea pigs form strong bonds with their human companions and other guinea pigs, making this a rewarding period for pet owners to enjoy their pets’ affectionate and interactive nature.
Senior Years (4 years and older)
Senior years in guinea pigs begin around four years of age and can extend to seven years or more, depending on their health and care. As they age, guinea pigs may experience a decline in activity levels and the onset of age-related health issues such as arthritis, dental problems, or decreased mobility. Providing a comfortable living environment, tailored nutrition, and regular veterinary care is essential to address these challenges. Senior guinea pigs often become more docile and enjoy gentle handling and interaction, offering a unique and rewarding bond with their caregivers during their later years.
Guinea Pig Diet and Nutrition
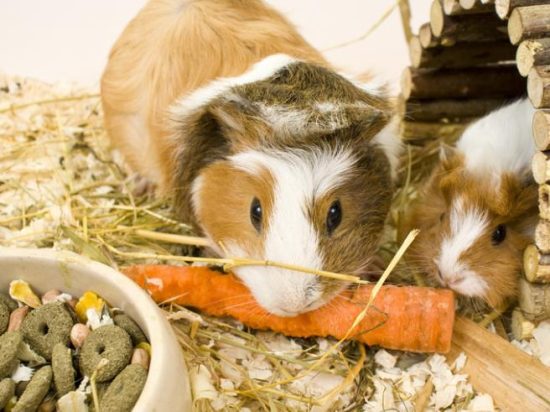

A balanced diet is crucial for the overall health and longevity of guinea pigs. The majority of their diet should consist of high-quality hay, such as Timothy hay, which helps maintain healthy digestion and wear down their constantly growing teeth. Fresh vegetables, such as leafy greens, carrots, and bell peppers, should also be provided daily to ensure they receive the necessary vitamins and minerals, including vitamin C.
Hay as the Primary Source of Fiber
Hay, especially Timothy hay, should make up the foundation of a guinea pig’s diet. It provides the essential fiber that helps maintain their digestive system and keeps their teeth healthy. Guinea pigs have continuously growing teeth, and the abrasive nature of hay helps wear them down, preventing dental issues.
Fresh Vegetables and Vitamin C
In addition to hay, guinea pigs require a variety of fresh vegetables to meet their nutritional needs. Leafy greens, such as kale, spinach, and romaine lettuce, are excellent sources of vitamins and minerals, including the crucial vitamin C. Carrots, bell peppers, and other crunchy vegetables can also be offered to provide a balanced diet.
Pellets for Supplementation
While hay and fresh vegetables should be the primary components of a guinea pig’s diet, high-quality guinea pig pellets can be provided in moderation to supplement their nutritional requirements. Pellets are formulated to contain the necessary vitamins, minerals, and protein that guinea pigs need. However, it’s essential to ensure that pellets do not make up the majority of their diet, as they can lead to obesity and other health issues if overconsumed.
Providing a proper diet, including a constant supply of fresh water, is essential for maintaining the health and well-being of these furry companions.
Living Environment and Exercise

Guinea pigs are active animals that require a spacious living environment to explore and play. Providing them with a large guinea pig enclosure where they can move around freely is essential for their physical and mental well-being. Adding tunnels, ramps, and various guinea pig toys can help keep them entertained and stimulated, preventing boredom and promoting a longer and healthier life.
Spacious Enclosure for Exploration
A spacious guinea pig living environment allows these furry companions to exercise and engage in natural behaviors. The enclosure should be large enough for them to move around freely, with ample room for running, jumping, and exploring. Incorporating different levels, platforms, and hiding spots can encourage natural behaviors and provide mental stimulation.
Toys and Enrichment for Mental Stimulation
Incorporating a variety of guinea pig toys and enrichment items can greatly enhance their living environment. Providing tunnels, hay racks, and chew toys not only satisfies their natural instincts but also helps prevent boredom and promotes a longer, healthier life. Regular exercise and a stimulating environment are crucial for maintaining the overall well-being of guinea pigs.
Ensuring a clean and stress-free guinea pig living environment, with proper ventilation and bedding, can also contribute to the overall health and longevity of these furry pets. By creating a comfortable and engaging space, owners can support their guinea pigs’ physical and mental well-being, ultimately extending their lifespan.
Common Health Issues and Signs of Aging
While guinea pigs are generally hardy animals, they are susceptible to certain health conditions that can impact their lifespan. Staying vigilant and addressing these issues promptly is crucial for ensuring your furry companion’s well-being.
Dental Problems
Dental problems are a common health issue in white guinea pigs, largely due to their continuously growing teeth. Malocclusion, where the teeth do not align properly, can lead to overgrown incisors or molars. Signs of dental issues include difficulty eating, weight loss, drooling, and visible misalignment of the teeth. Regular veterinary check-ups and providing appropriate chew toys and fibrous foods, such as hay, can help prevent and manage dental problems. It’s important to address dental issues promptly to avoid severe pain and secondary health complications.
Respiratory Infections
Respiratory infections are another common health concern in white guinea pigs, often caused by bacteria such as Bordetella or Streptococcus. Symptoms include sneezing, coughing, nasal discharge, and labored breathing. These infections can quickly become serious, leading to pneumonia if not treated promptly. Factors such as poor ventilation, dirty living conditions, and stress can increase the risk of respiratory infections. Ensuring a clean and well-ventilated habitat, minimizing stress, and seeking veterinary care at the first sign of respiratory distress are crucial for maintaining respiratory health.
Skin Conditions
White guinea pigs are prone to various skin conditions, including fungal infections (such as ringworm), parasitic infestations (mites or lice), and allergies. Symptoms include itching, hair loss, redness, scabs, and flaky skin. Regular grooming and observation are essential to catch early signs of skin problems. Maintaining a clean environment and providing a balanced diet rich in vitamin C can help prevent skin issues. If a skin condition is suspected, prompt veterinary diagnosis and treatment are necessary to relieve discomfort and prevent the spread of infections.
Urinary Tract Problems
Urinary tract problems, such as urinary tract infections (UTIs) and bladder stones, are common in white guinea pigs. Signs include frequent urination, blood in the urine, straining to urinate, and abdominal discomfort. These issues can be exacerbated by a diet high in calcium or poor hydration. Ensuring your guinea pig has access to fresh water at all times and providing a balanced diet with appropriate calcium levels can help prevent urinary problems. If symptoms of a urinary tract issue are observed, immediate veterinary attention is needed to diagnose and treat the condition effectively, preventing further complications.
Weight Loss and Reduced Activity
As guinea pigs age, they may start to exhibit signs of reduced activity levels and weight loss. These changes can be indicative of underlying health issues or the natural aging process. Closely monitoring your guinea pig’s appetite, weight, and energy levels can help identify any concerns and ensure they receive the necessary care and attention during their senior years.
By staying vigilant and addressing these common health issues promptly, you can help ensure your guinea pig enjoys a longer and more comfortable life. Regular veterinary check-ups and a proactive approach to their care can go a long way in promoting the overall well-being of these beloved pets.
How long do guinea pigs live?
Guinea pigs have an average lifespan of 5 to 7 years, although some can live up to 10 years or even longer with proper care and attention. Factors such as genetics, diet, exercise, and living environment can all influence a guinea pig’s longevity. Understanding the different stages of a guinea pig’s life, from infancy to senior years, and providing them with the necessary care and resources can help ensure they live a long and healthy life.
| Breed | Average Lifespan |
|---|---|
| Skinny Guinea Pig | 7 to 8 years |
| Abyssinian Satin Guinea Pig | 4 to 6 years |
| American Guinea Pig | 5 to 7 years |
| Silkie Guinea Pig | 6 to 8 years |
While the average lifespan for guinea pigs is around 5 to 7 years, different breeds can have variations in their life expectancy. Factors such as genetics, breed-specific health concerns, and the level of care provided can all contribute to these lifespan variations. Researching the average lifespan of different guinea pig breeds can help potential owners make informed decisions when choosing their furry companion.
Extending the Lifespan of Guinea Pigs
While genetics play a significant role in determining a guinea pig’s lifespan, there are several steps owners can take to extend their furry friend’s life expectancy. Providing a balanced diet rich in hay, fresh vegetables, and high-quality pellets, along with ensuring they have access to clean, fresh water, is crucial for maintaining their overall health and longevity.
Balanced Diet and Hydration
Encouraging a diet that includes a variety of hay, such as Timothy or orchard grass, as the primary source of fiber is essential for supporting a guinea pig’s digestive health. Supplementing their diet with fresh, nutrient-dense vegetables like leafy greens, carrots, and bell peppers can also help fulfill their vitamin and mineral needs. Additionally, a moderate amount of high-quality guinea pig pellets can provide essential nutrients to complement their natural plant-based diet. Ensuring a constant supply of clean, fresh water is also vital for maintaining proper hydration and overall well-being.
Regular Exercise and Enrichment
Promoting regular exercise and mental stimulation is another important factor in extending a guinea pig’s lifespan. Providing them with a spacious enclosure that allows for exploration and play can help keep them active and engaged. Incorporating various toys, tunnels, and other enrichment items can also contribute to their overall physical and mental well-being, reducing the risk of boredom and inactivity.
Veterinary Care and Monitoring
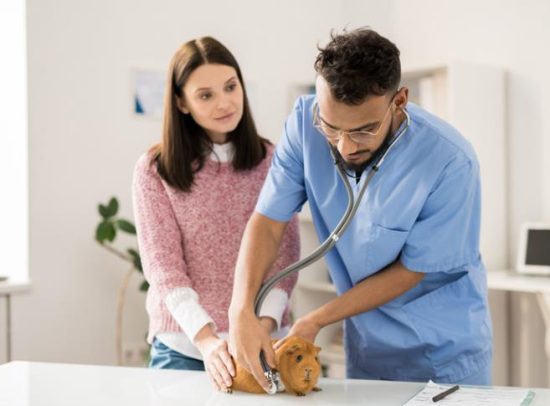

Regular veterinary check-ups are essential for detecting and addressing any potential health issues early on, allowing for prompt treatment and prevention of complications. Monitoring your guinea pig’s weight, appetite, and overall behavior can also help identify any signs of illness or aging, enabling you to seek professional medical attention if necessary. By following these guidelines and providing your guinea pig with the necessary care and attention, you can help ensure they live a long and fulfilling life.
Guinea Pig Breeds and Lifespan Variations
Different guinea pig breeds can have notable variations in lifespan. While the average lifespan of a guinea pig is around 5 to 7 years, some breeds may live significantly longer or shorter lives. For instance, Skinny guinea pigs have an average lifespan of 7 to 8 years, whereas Abyssinian Satin guinea pigs typically live between 4 to 6 years.
Factors such as genetics, breed-specific health concerns, and the level of care provided can all contribute to these lifespan variations among guinea pig breeds. Researching the average lifespan of different guinea pig breed options can help potential owners make informed decisions when choosing their furry companion and ensure they select a breed suitable for their lifestyle and commitment level.
| Guinea Pig Breed | Average Lifespan |
|---|---|
| Skinny Guinea Pig | 7-8 years |
| Abyssinian Satin Guinea Pig | 4-6 years |
| Silkie Guinea Pig | 5-7 years |
| American Guinea Pig | 5-7 years |
| Teddy Guinea Pig | 6-8 years |
By understanding the lifespan of different guinea pig breeds, owners can make informed decisions and provide the appropriate level of care and attention to ensure their furry friends live long, healthy, and fulfilling lives.
Myths and Misconceptions
There are several myths and misconceptions surrounding guinea pig lifespans. One common misconception is that guinea pigs only live for a few years, when in reality, they can live up to 8, 10 years or even longer with proper care. Another myth is that male guinea pigs have shorter lifespans than females, but there is no scientific evidence to support this claim. Additionally, some people believe that guinea pigs don’t need veterinary care, which is not true. Regular check-ups with a veterinarian are essential for ensuring the overall health and well-being of these furry companions.
Debunking these guinea pig lifespan myths and common guinea pig lifespan misconceptions can help ensure that guinea pig owners provide their pets with the necessary care and attention to help them thrive.
| Myth | Reality |
|---|---|
| Guinea pigs only live for a few years. | Guinea pigs can live up to 8-10 years or longer with proper care. |
| Male guinea pigs have shorter lifespans than females. | There is no scientific evidence to support this claim. |
| Guinea pigs don’t need veterinary care. | Regular veterinary check-ups are essential for the health and well-being of guinea pigs. |
FAQs on how long do Guinea pigs live
How long do guinea pigs live as a pet?
The average lifespan of domesticated guinea pigs is typically 5 to 7 years, with some reaching up to 10 years or even longer with proper care and attention.
Can a guinea pig live for 12 years?
While it is possible for some guinea pigs to live up to 10 years or even longer, the average lifespan is 5 to 7 years. Reaching 12 years old is quite rare and would require exceptional care and genetics.
Do indoor guinea pigs live longer?
Yes, guinea pigs kept as indoor pets generally live longer than those kept outdoors. Indoor guinea pigs are protected from environmental factors, such as extreme temperatures, predators, and potential injuries, which can all contribute to a shorter lifespan.
Is a 3 year old guinea pig old?
No, a 3 year old guinea pig is not considered old. Guinea pigs typically reach adulthood between 1 to 4 years of age, and they are generally considered in their prime during this time. As they approach 4 years and older, they are entering their senior years.
Can guinea pigs live alone if one dies?
Guinea pigs are social animals and do not thrive well when kept alone, even if one of their companions passes away. It is generally recommended to have at least two guinea pigs to provide companionship and prevent loneliness and stress.
How old is a 7 year old guinea pig in human years?
There is no direct conversion between guinea pig years and human years, as the aging process differs between species. However, a 7 year old guinea pig would be considered quite senior and may require more specialized care and attention as they approach the upper end of their lifespan.
Is 1 old for a guinea pig?
No, 1 year old is not considered old for a guinea pig. Guinea pigs generally reach adulthood and their prime between 1 to 4 years of age. They are considered in their senior years at around 4 years and older.
What is the oldest living guinea pig?
The oldest known guinea pig on record lived to be around 14 years old. However, this is an exceptional case, and the average lifespan for most domesticated guinea pigs is between 5 to 7 years, with some reaching up to 10 years with proper care and attention.








